Nucleic Acids
Nucleic Acids: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Nucleic Acids, Heredity, DNA, RNA (Ribonucleic Acids), Nitrogenous Bases, Beta-D-Ribose, Beta-D-2-Deoxyribose, Nucleosides, Nucleotides, Phosphodiester Linkage, Dinucleotide, Polynucleotide, and Inorganic Phosphate.
Important Questions on Nucleic Acids
Which one of the following base in not present in DNA?
In both DNA and RNA, heterocylic base and phosphate ester linkages are at
Which of the following is not true about DNA and RNA?
Describe the structural features of nucleic acids.
Nucleic acids are the polymers of Nucleotides.
What products would be formed when a nucleotide from DNA containing thymine is hydrolysed?
The number of primary and secondary hydroxyl groups in ribose are _______ respectively.
In nucleic acid, the sequence is base-phosphate-sugar.
The average energy of each hydrogen bond in pair is and that in pair is . Assuming that no other interaction exists between the nucleotides, the approximate energy required in to split the following double stranded into two single strands is
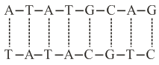
[Each dashed line may represent more than one hydrogen bond between the base pairs]
The process of RNA _____ helps in putting together the sequence of exons to form a mature mRNA molecule.
Define heredity. Differentiate between DNA and RNA(any 2 points).
Which of the following molecules transmit characters from parents to offpsrings in heredit?
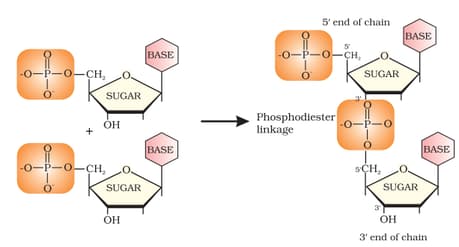
Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage.
Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage between _____ carbon atoms of the pentose sugar.